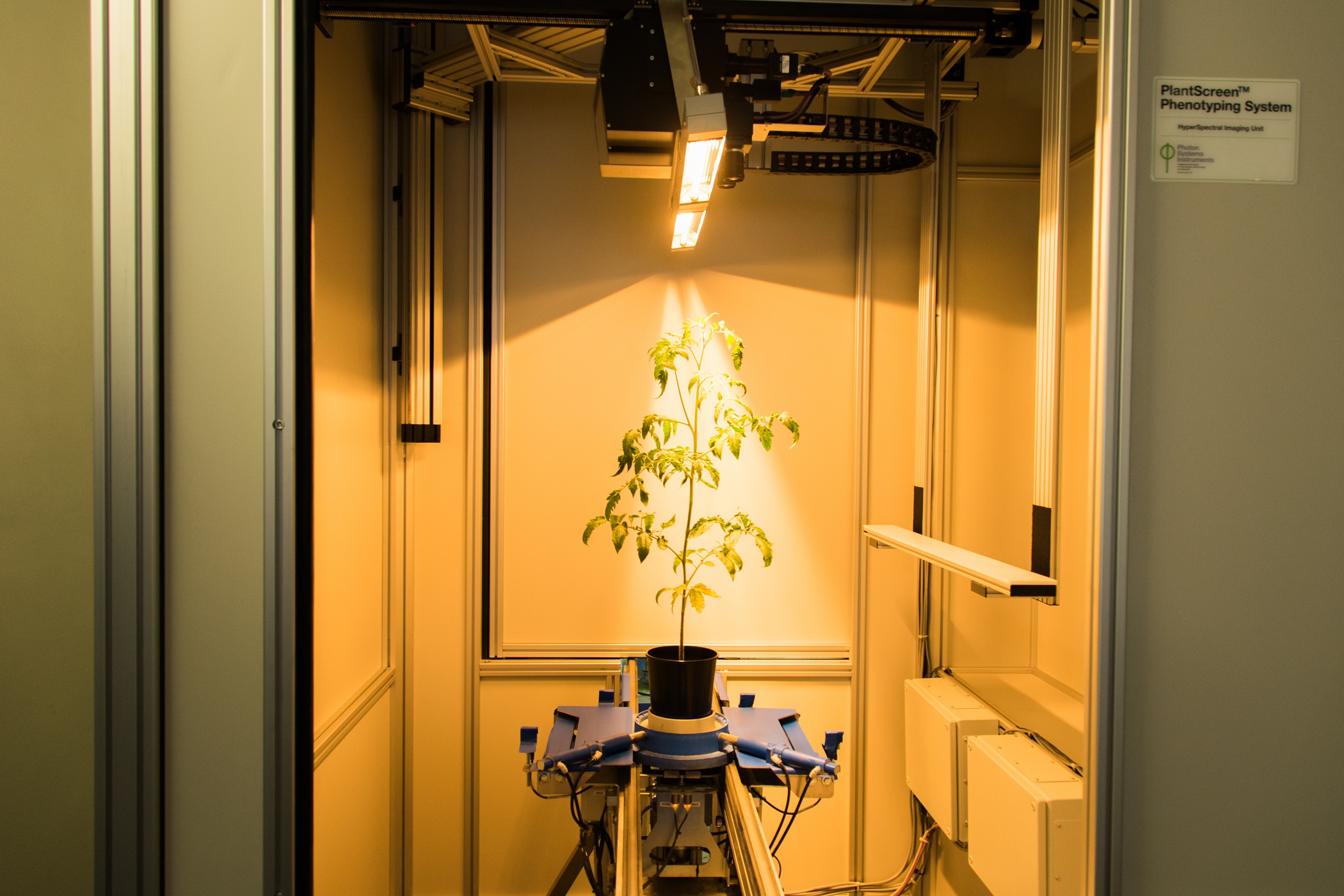
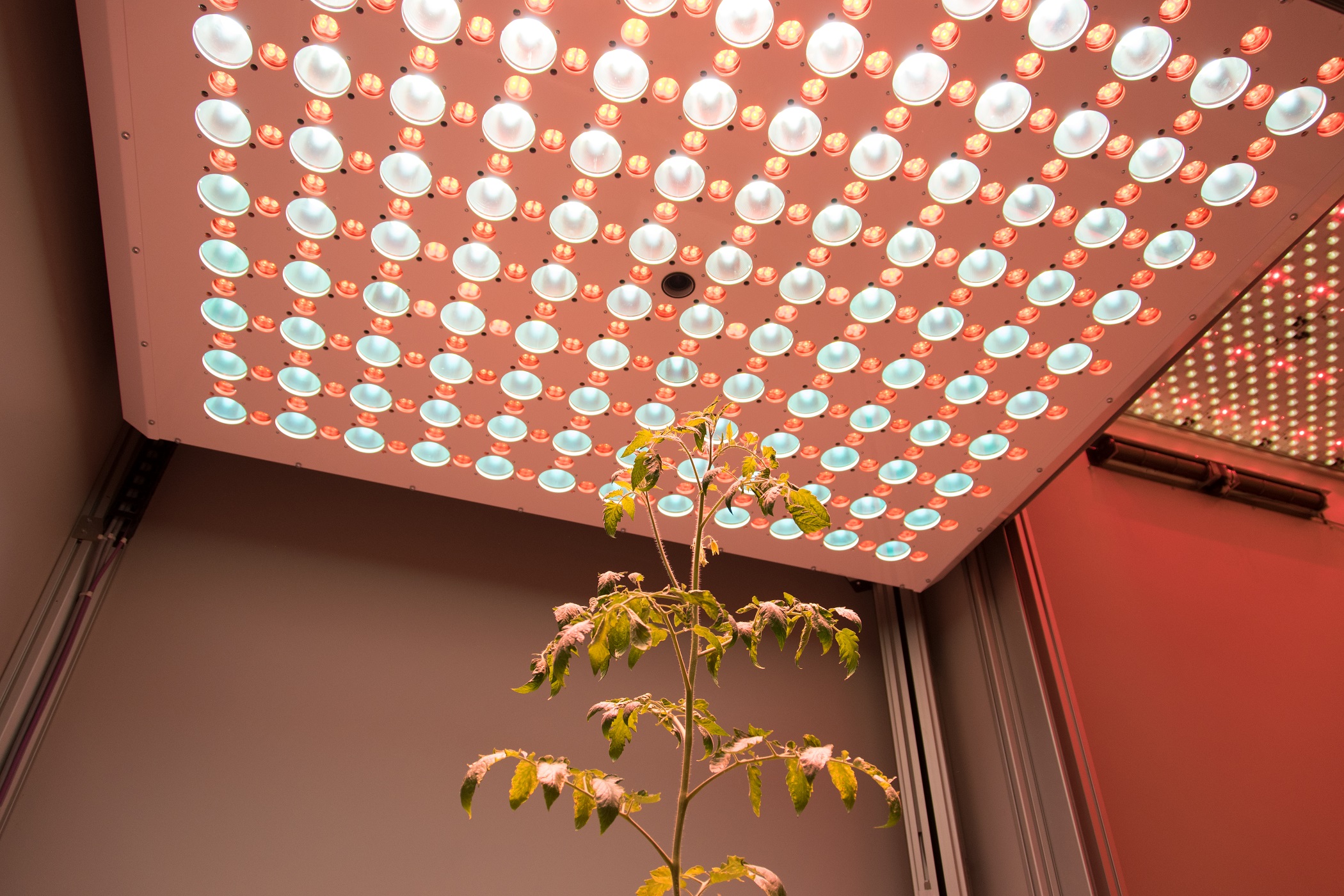
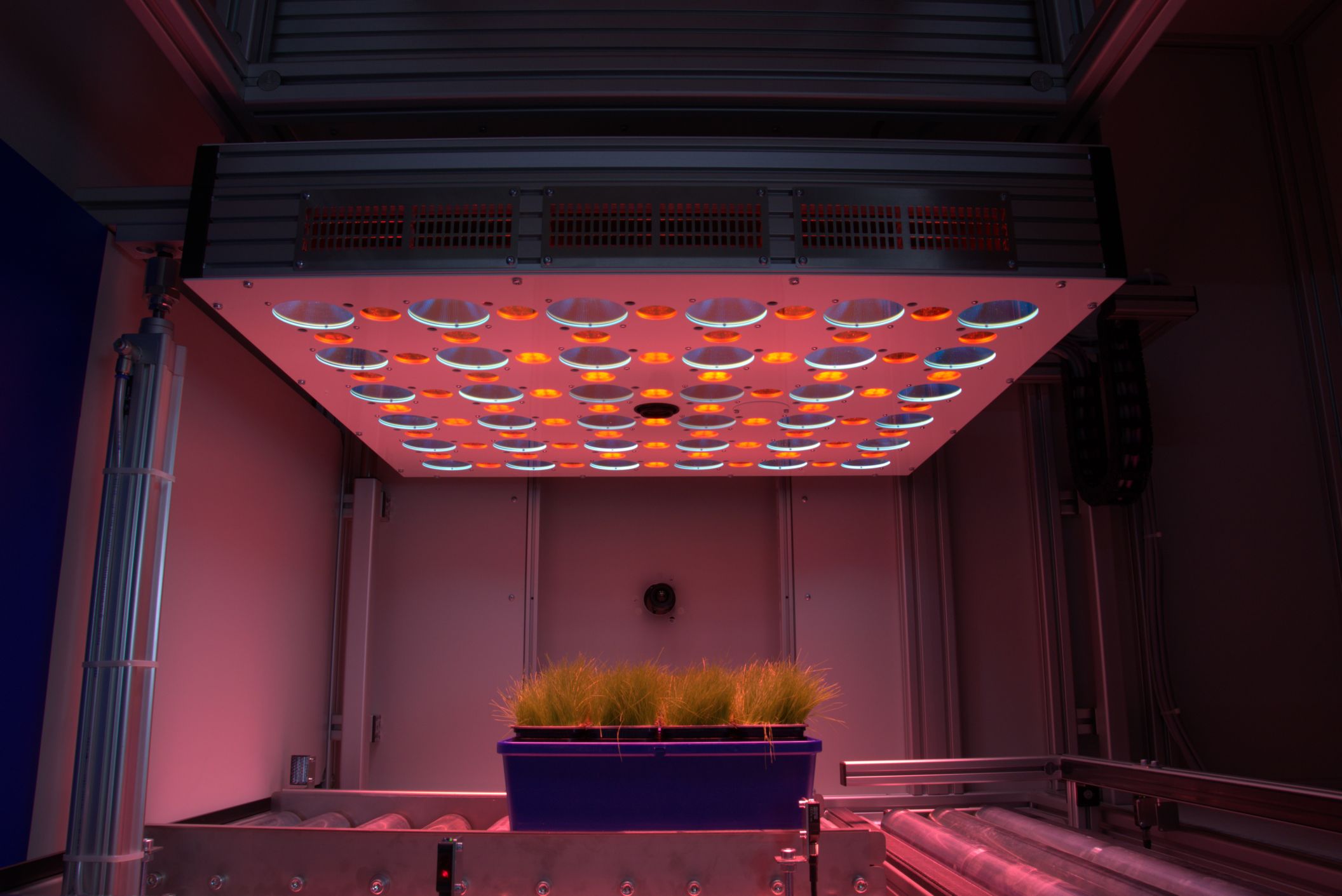
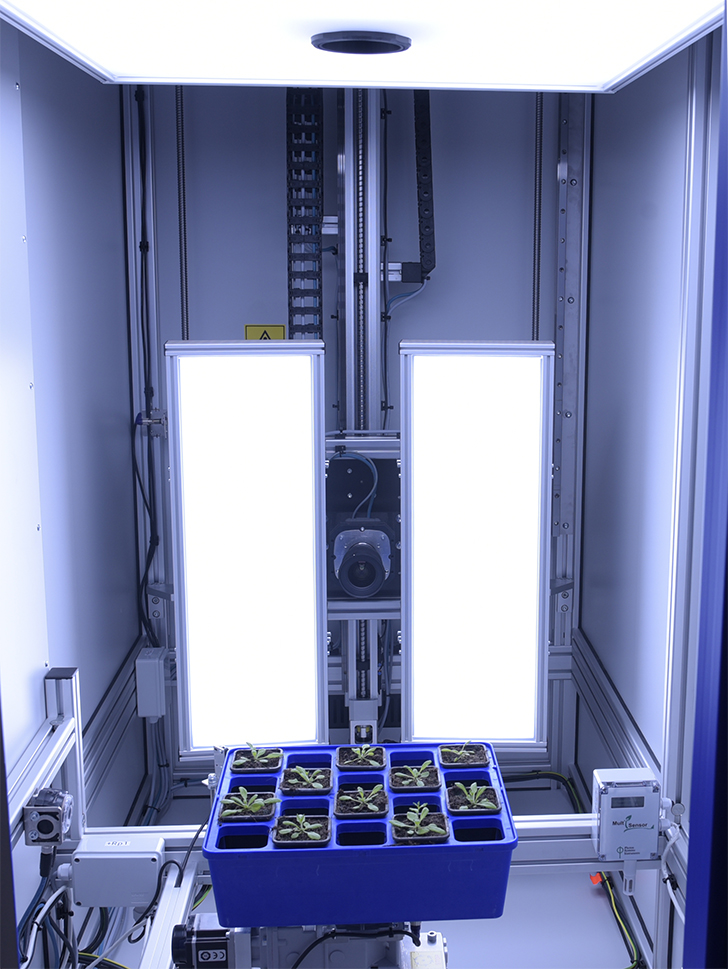
PlantScreenTM Imaging Sensors are complete integrated solutions for non-invasive analysis of plant specific patterns of absorption, emission and reflection. Digital trait assesment sensors are based on analysis of wide range of electromagnetic radiation wavelength bands: visible range of spectra is detected by RGB cameras for structural and color analysis, hyperspectral cameras in visible, near-infrared and short wavelength infra-red range of spectra are used for reflectance-based analysis of plants, thermal imaging cameras are optimized for leaf temperature and stomata conductance analysis, kinetic chlorophyll fluorescence imaging sensors for analysis of plant photosynthetic performance.
- Range of high-end sensors
- Sensor-specific light sources
- Light-isolated imaging box
- Multiple angle imaging
- Sensor-specific raw data processing software
- Comprehensive software package
- Customized solutions
RGB and Morphometric Imaging
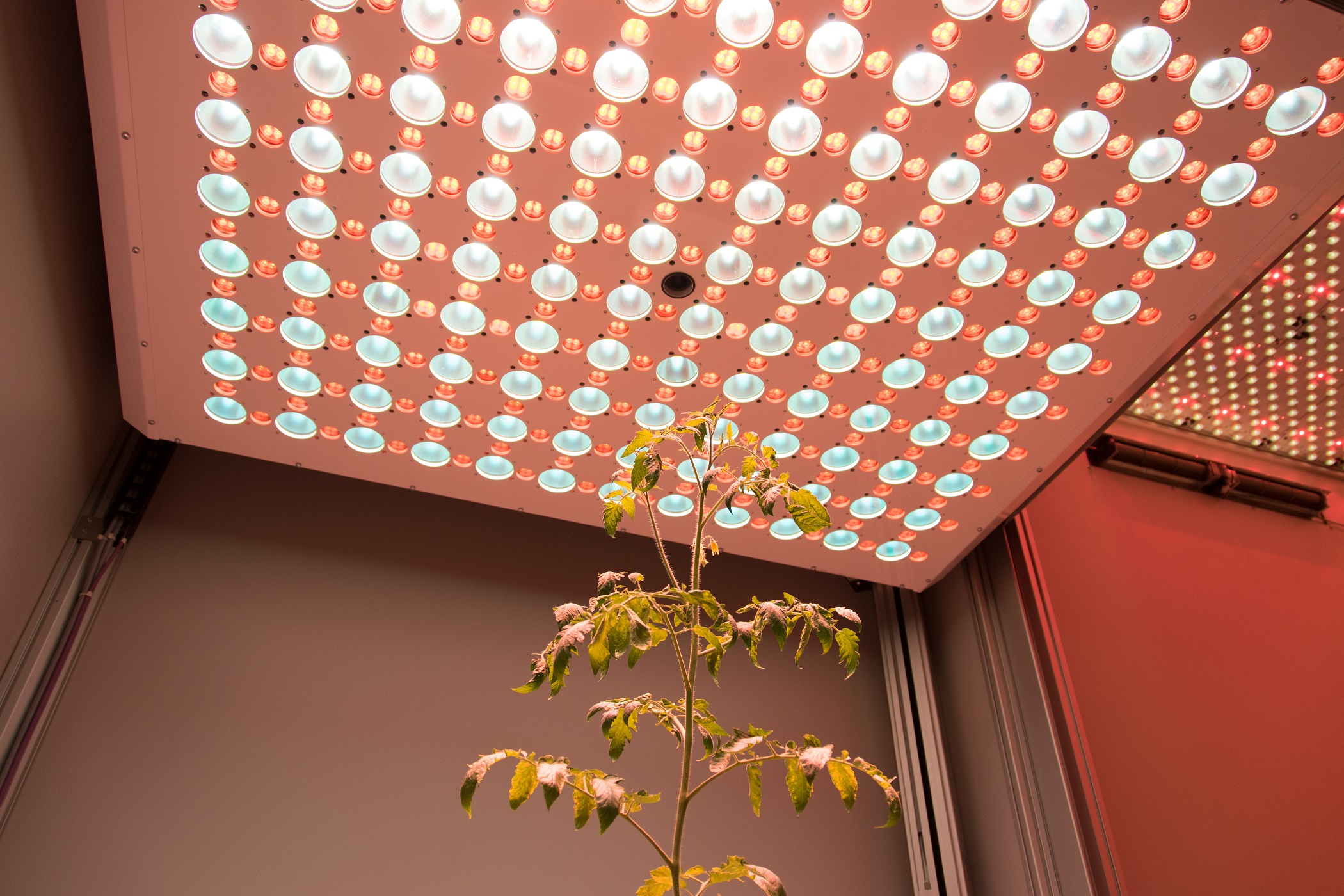
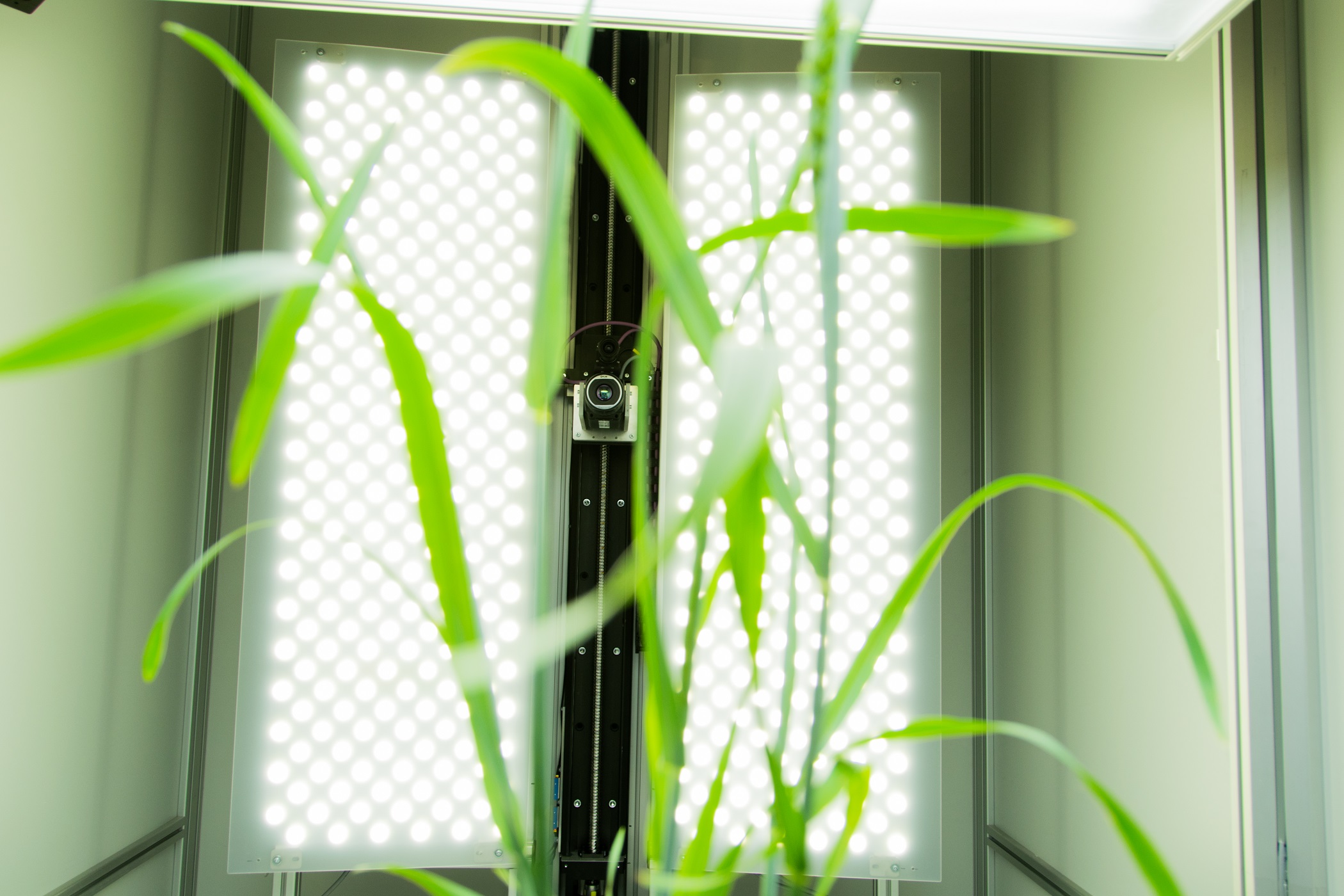
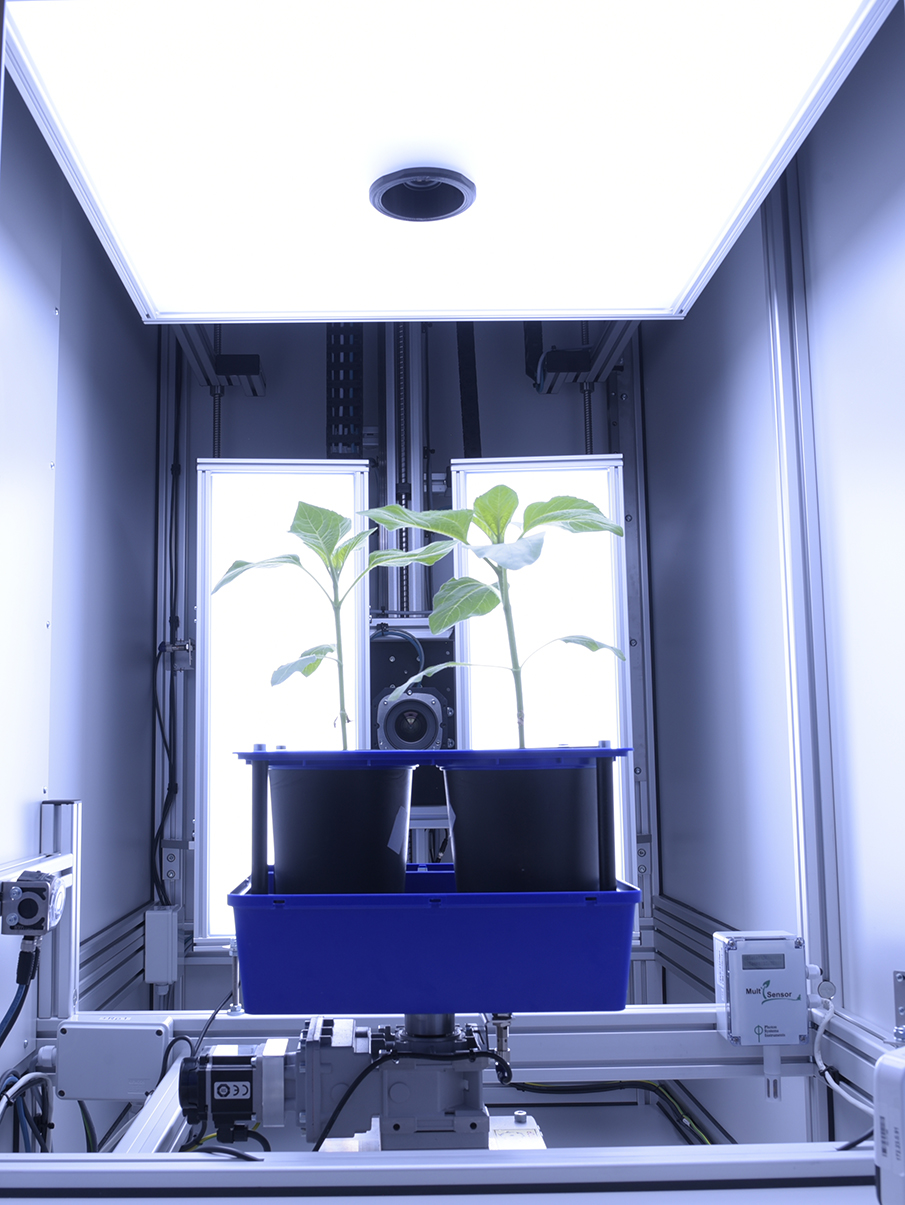
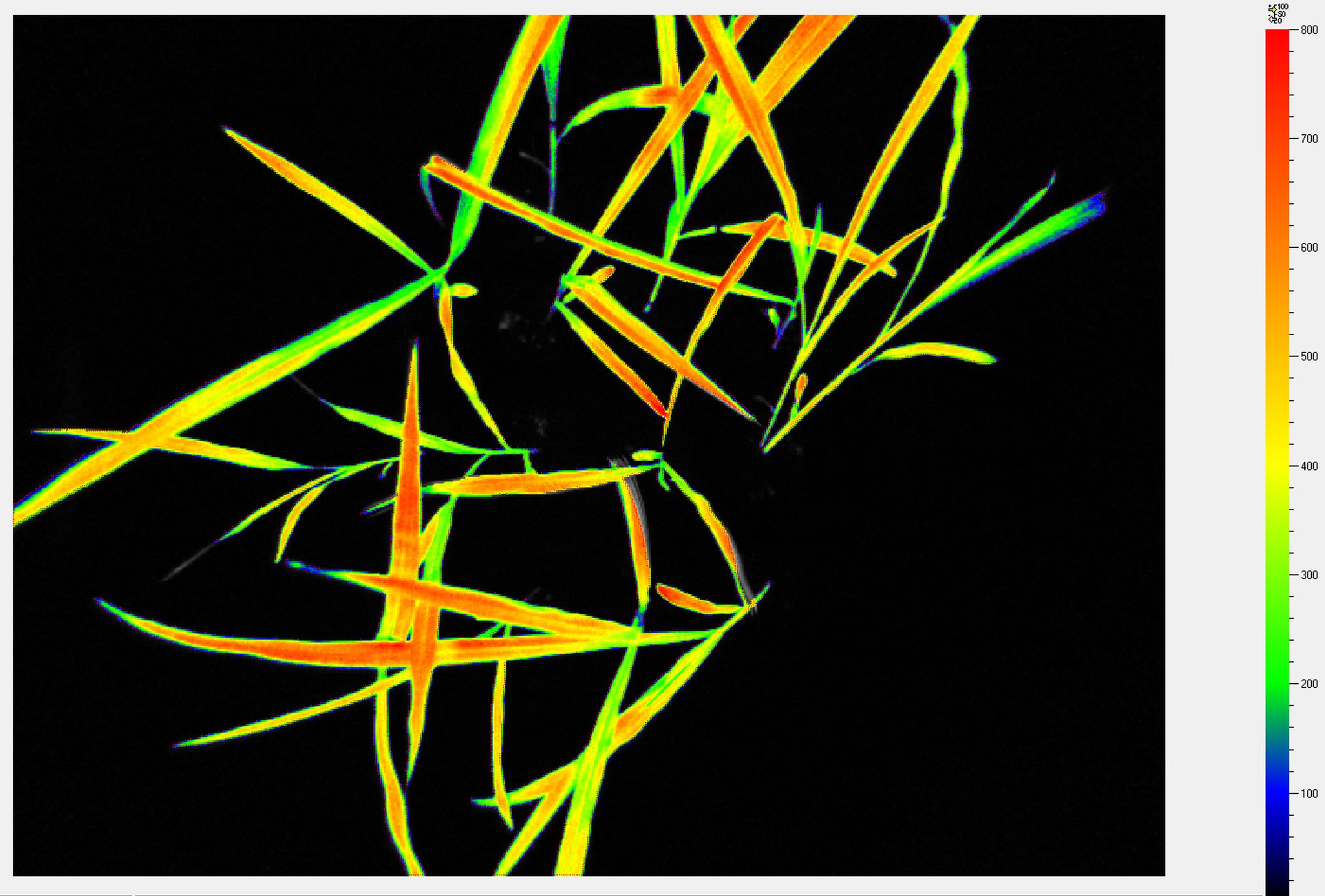
Wide range number of features linked to plant growth and development can be extracted from digital colour RGB imaging or 3D scanning technology, when connected to the automatic software analysis. RGB digital imaging applied in high resolution is used for in-depth analysis of plant morphology, architecture and colour index analysis.
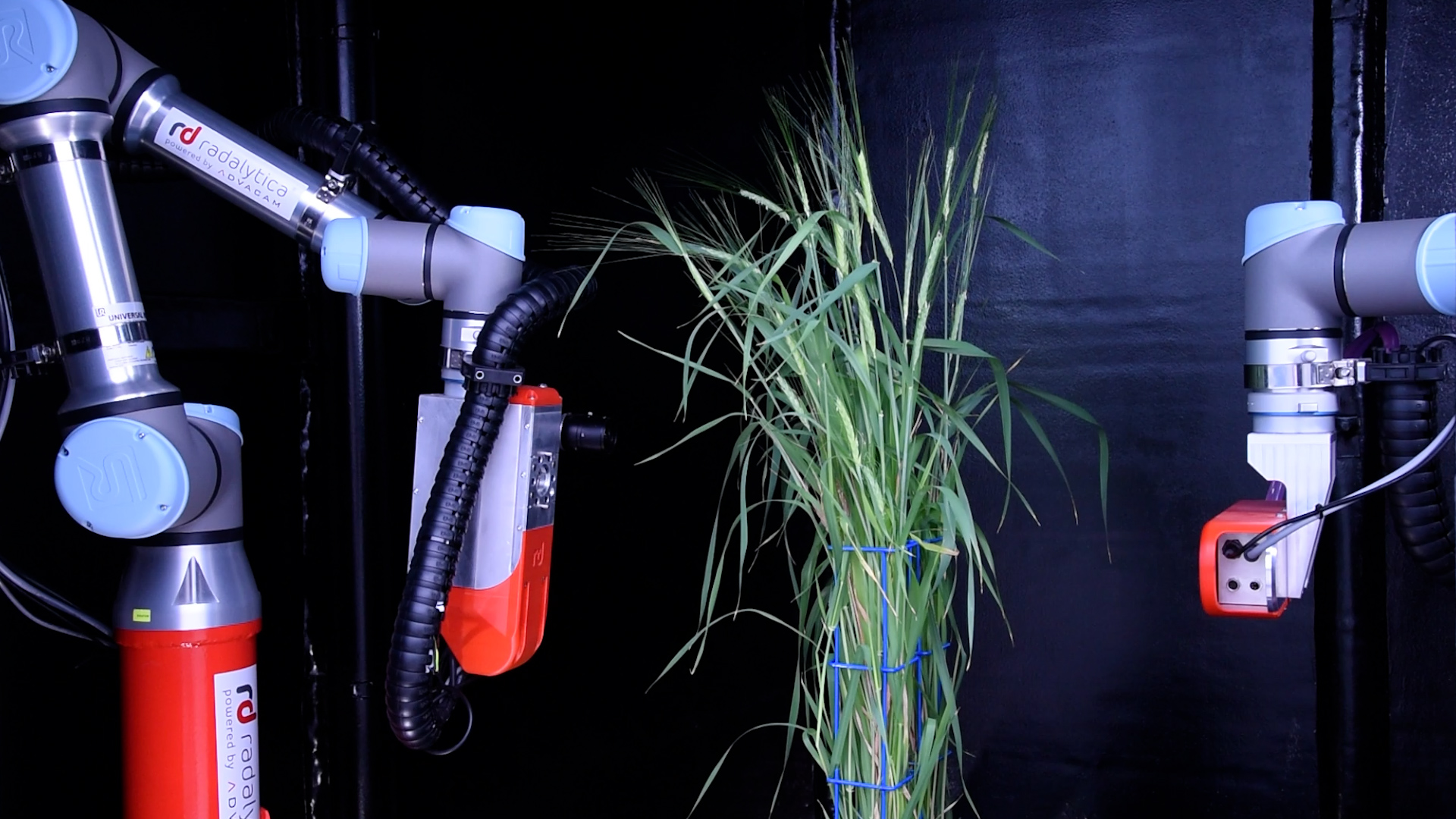
Industrial high performance cameras with a Gbit Ethernet connection are mounted on robotic arm together with the white LED light source to ensure high speed data transfer and precise color separation. Cameras with high-sensitivity CCD-sensors, high-resolution and broad dynamic range are used.
Key features
- 2D or 3D scanning mode
- Top view up to 150 cm plant height
- Side view up to 150 cm plant height
- Side view in range 0-360°
- Line scanning mode for side view
- Species oriented analysis (mono and di-cotyledonous plants)
- Static and dynamic analysis
- Homogenous LED light source
Download the information brochure (pdf)
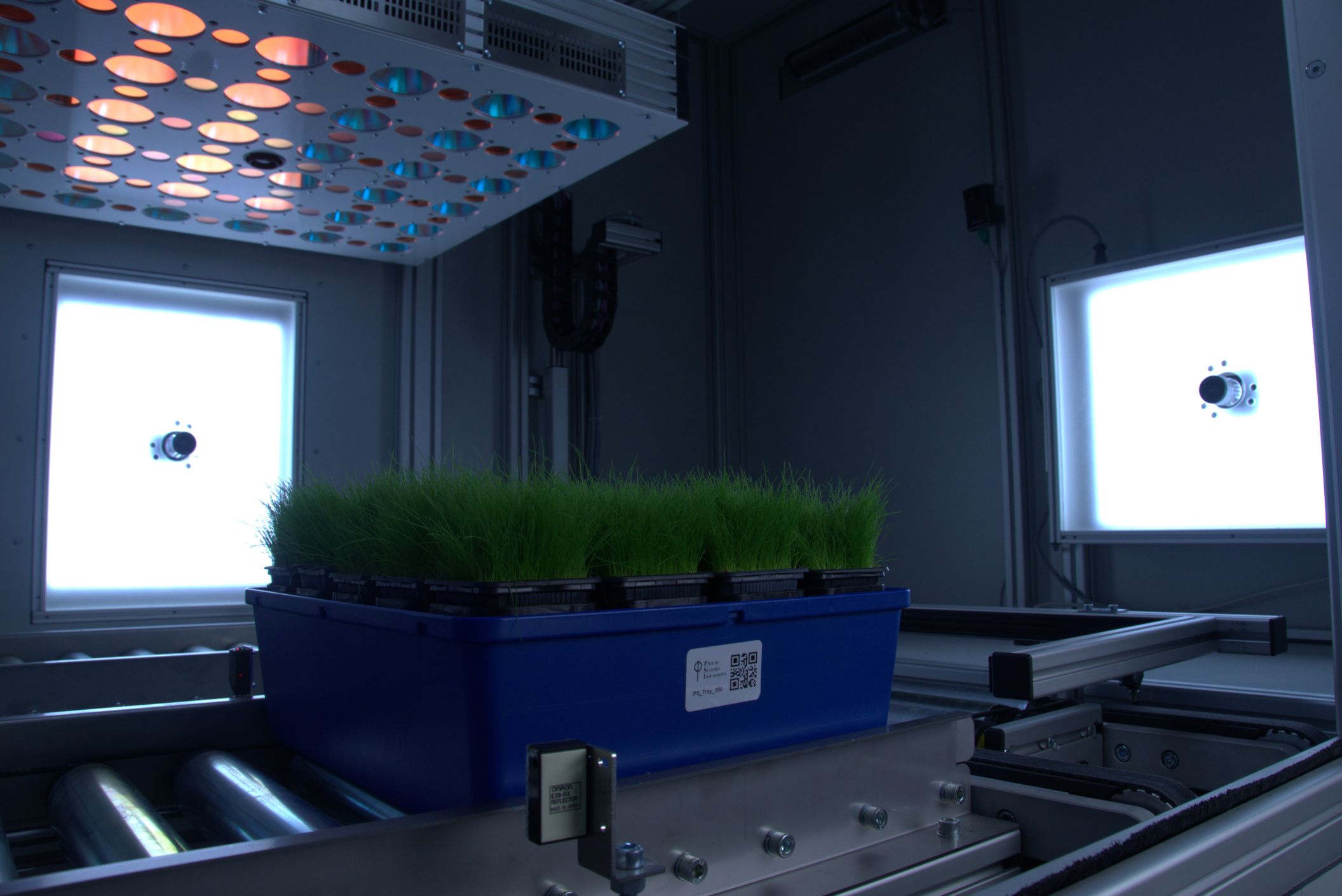
Kinetic chlorophyll fluorescence Imaging
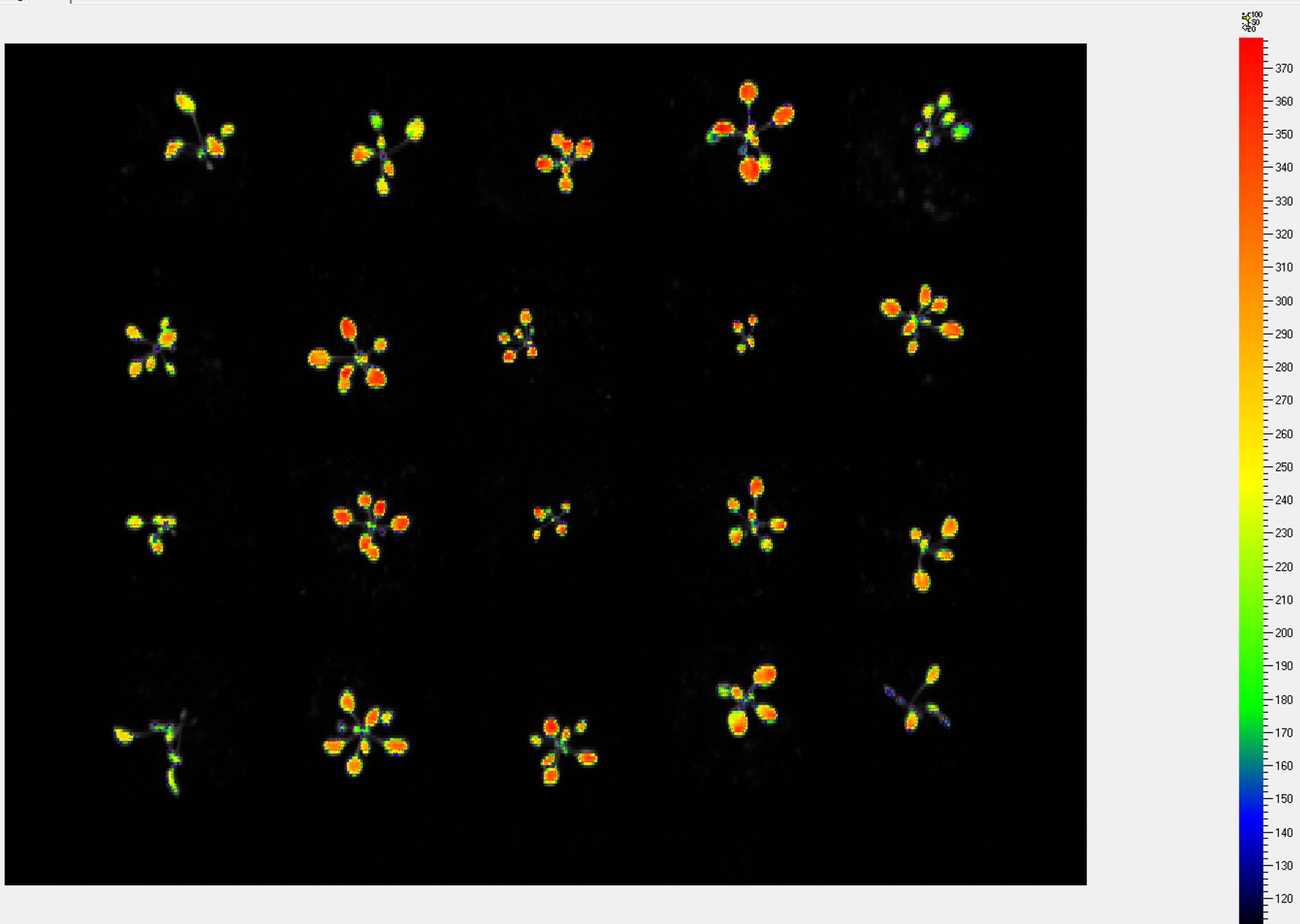
Chlorophyll fluorescence is popular technique in plant physiology used for rapid non-invasive measurement of photosystem II (PSII) activity. PSII activity is very sensitive to range of biotic and abiotic factors and therefore chlorophyll fluorescence technique is used as rapid indicator of photosynthetic performance of plants in different developmental stages and/or in response to changing environment. Systems developed by PSI monitor fluorescence kinetics in pulse-amplitude modulated mode, which provides a wealth of information about a plant’s photosynthetic capacity, physiological and metabolic condition, as well as its susceptibility to various stress conditions.
The advantage of chlorophyll fluorescence measurements over other methods for monitoring stresses is that changes in chlorophyll fluorescence kinetic parameters often occur before other effects of stress are apparent. The method is non-invasive, and the spread of inhibition can be observed and quantified with time. Heterogeneity in the location of inhibition is easily seen and quantified when using imaging systems to measure chlorophyll fluorescence. Chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics measured in the PlantScreenTM Phenotyping Systems provides a wealth of information about a plant’s photosynthetic capacity, physiological and metabolic condition, as well as its susceptibility to various stress conditions.
Key features
- High sensitivity CCD camera
- Multi-colour LED light panel
- Pulse-modulated short duration flashes for accurate measurement of minimal fluorescence (Fo value) determination
- Two types of actinic lights for light-adapted and quenching analysis with maximum light intensity reaching 2000 µmol.m-2.s-1.
- Saturating light pulse for maximal fluorescence Fm value determination with maximal light intensity up to 6000 µmol.m-2.s-1
- Additional light: FAR (735 nm) for determination of Fo'. Royal blue (450 nm) as excitation light source for GFP detection.
- Camera includes 7 position filter wheel, ChlF and GFP filter and other filter sets according to user’s needs.
- Custom-designed open FluorCam to image plant in trays and pots of various dimensions with maximum imaged area of 80 cm x 80 cm
- User defined programmable measuring protocols.
- Automatic data analysis and parameters computation
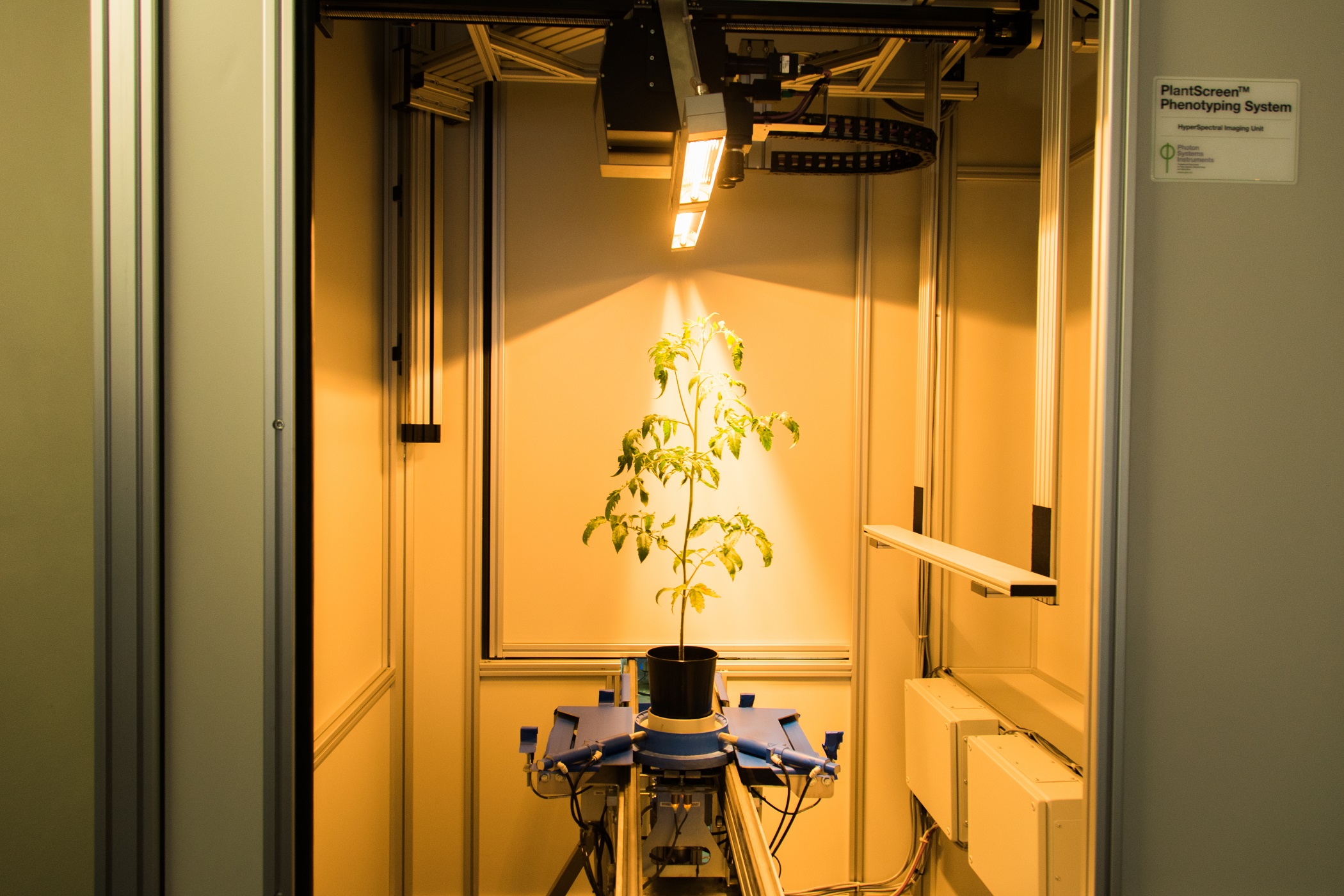
Hypespectral Imaging in visible and/or near-infrared region
Hyperspectral imaging has been used for many years to study patterns of plant growth from satellite imaging. This technology has been refined in PSI’s PlantScreenTM Phenotyping Systems to provide 3-dimensional hyperspectral data sets of plants on a pixel by pixel basis in spectral range from 400 to 2500 nm. Using a hyperspectral camera with image analysis software, plant reflective indices can be visualized across the entire surface of the imaged sample(s). These indices may be correlated with numerous physiological conditions , as well as the biochemical status of the plant or leaf with respect to the chlrophyll or pigment composition, water status or cell structure.
Hyperspectral cameras for both visible (VNIR) and short-wavelength infrared region (SWIR) of the spectrum are available. The cameras are mounted on robotic stage with dedicated illumination source for homogenous sample illumination. Full spectral scan across the entire spectral range of the camera for each pixel of the image can be acquired, optionally specific wavelengths of interest can be recorded that may be correlated with, for example, leaf nitrogen status, or the production of anthocyanin to protect Photosystem II under high light stress.
Key features
- Spectral range covers wavelengt from 400 to 2500 nm ( visible, near-infrared and short-wavelength of infrared region)
- Specific light illumination source
- Top and side view configuration possible
- Pixel-by –pixel spectral profile
- Line scanner operation
- Automatic calibration steps with reference object
- Programmable measuring protocols
- Automatic analysis of defined parameters
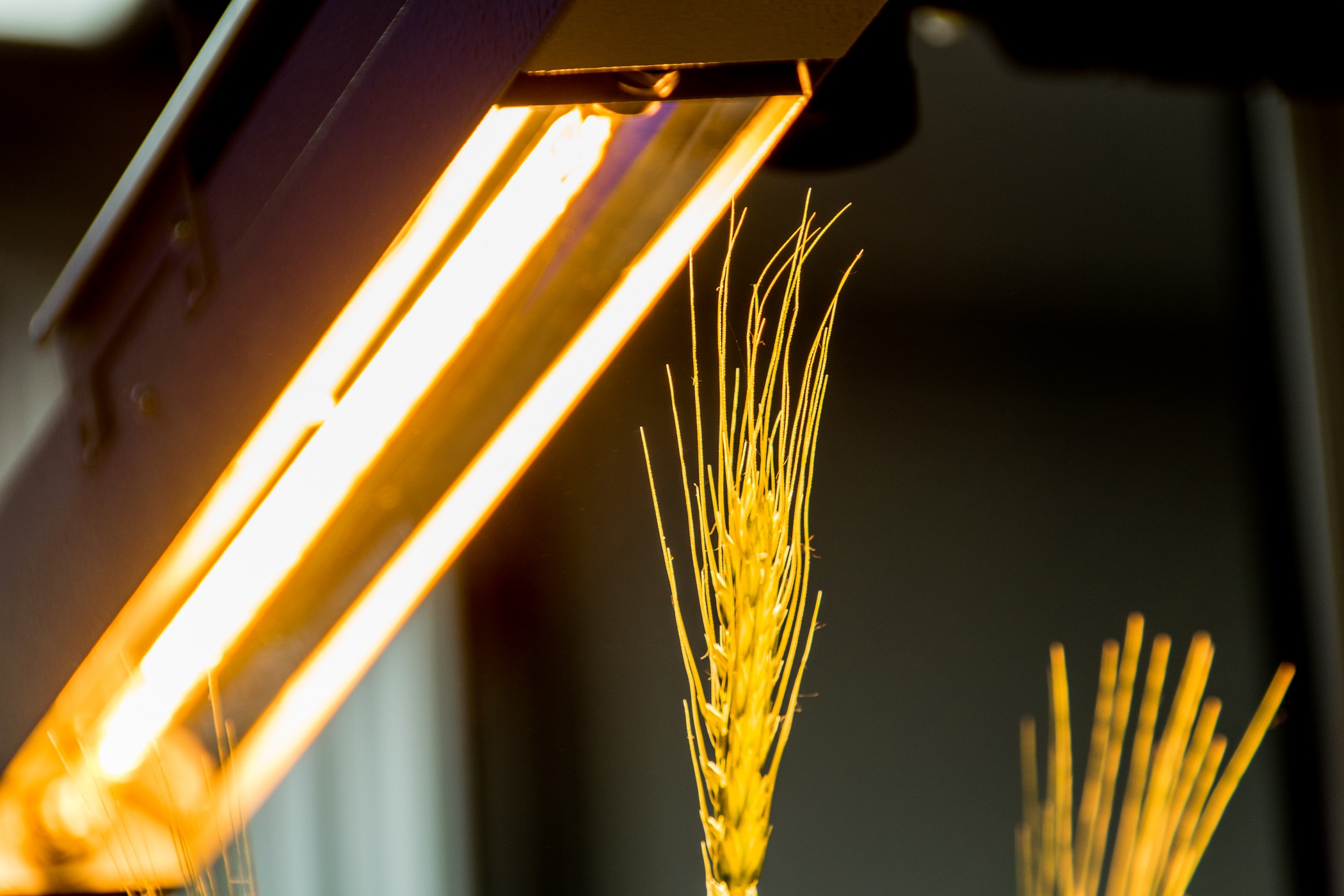
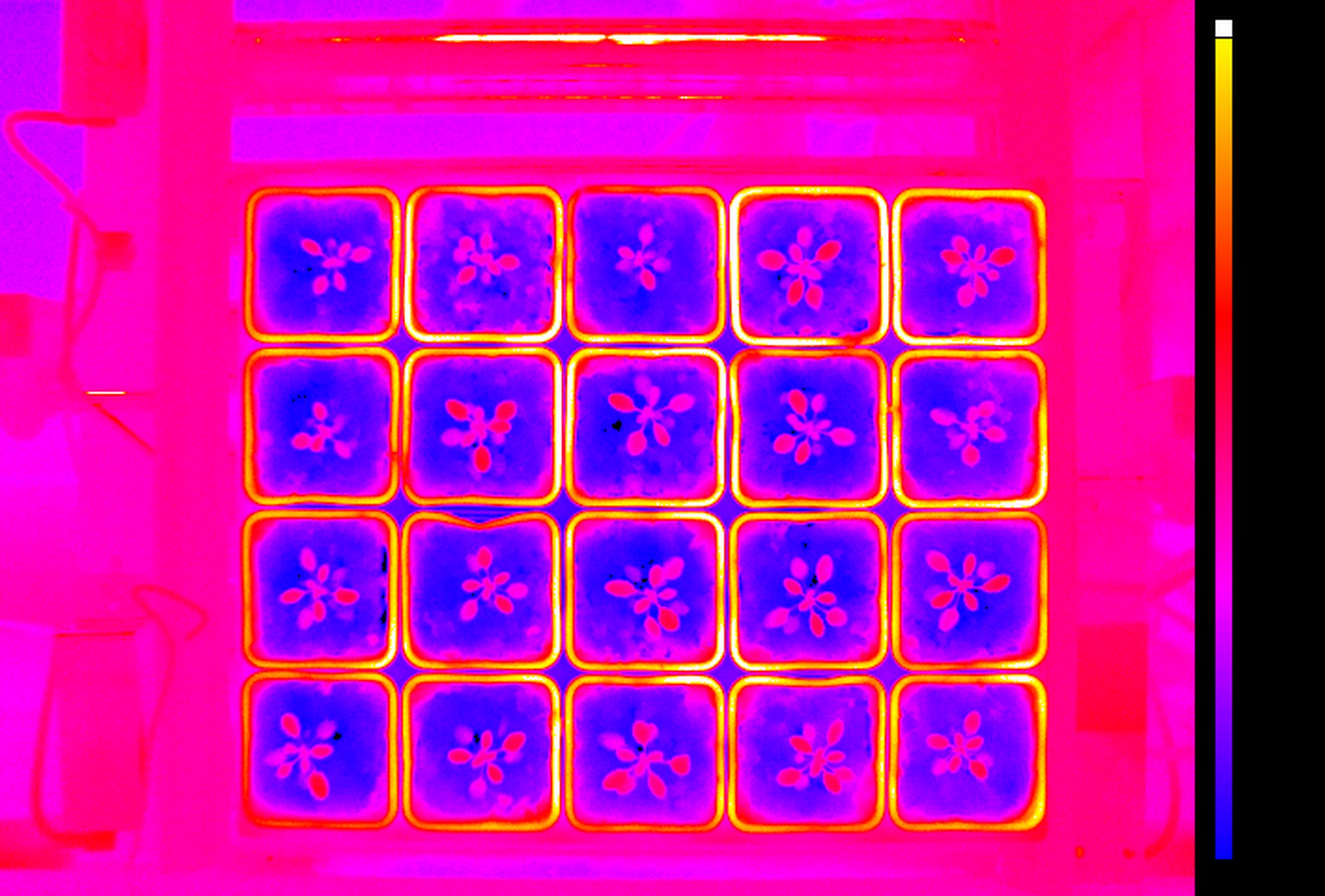
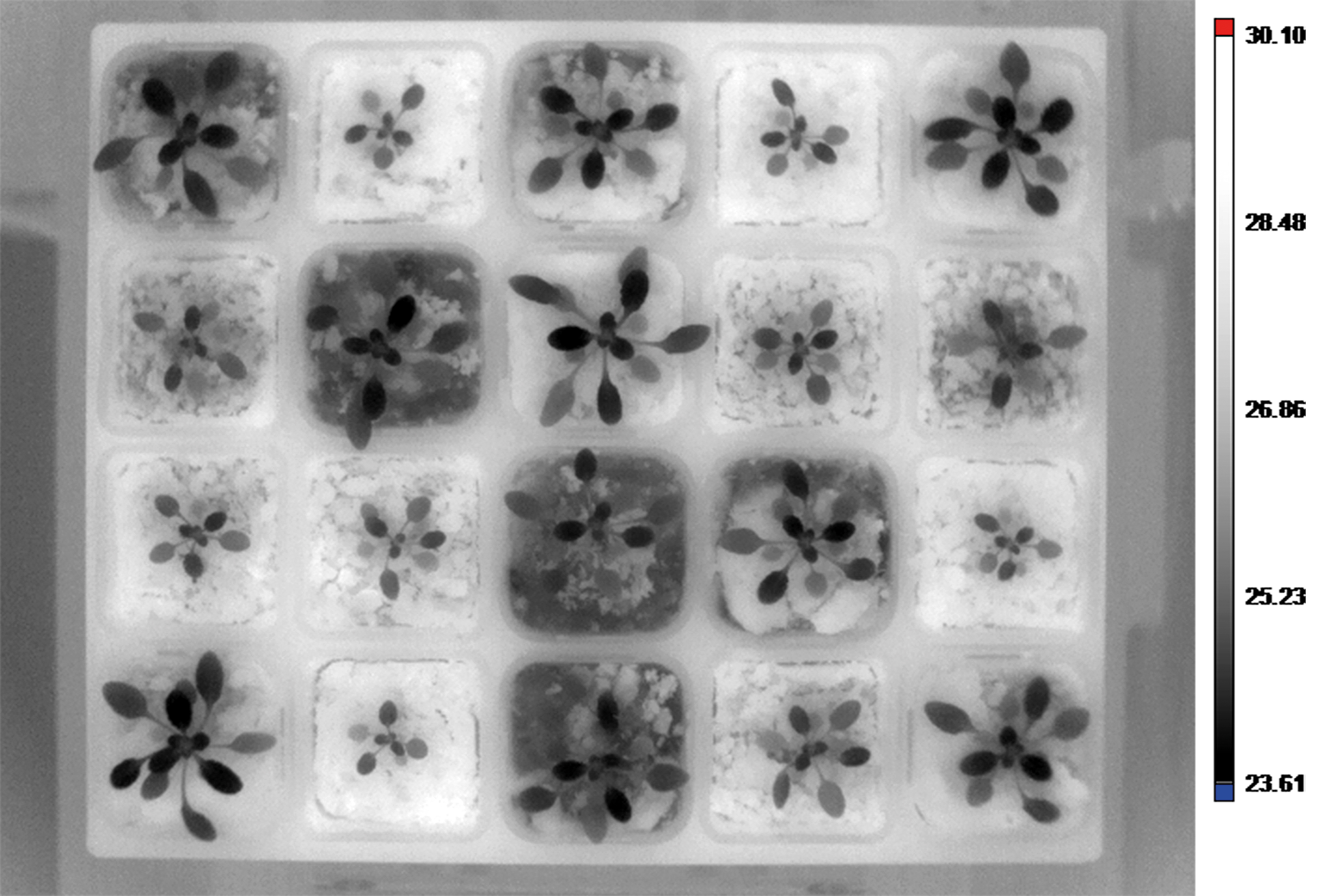
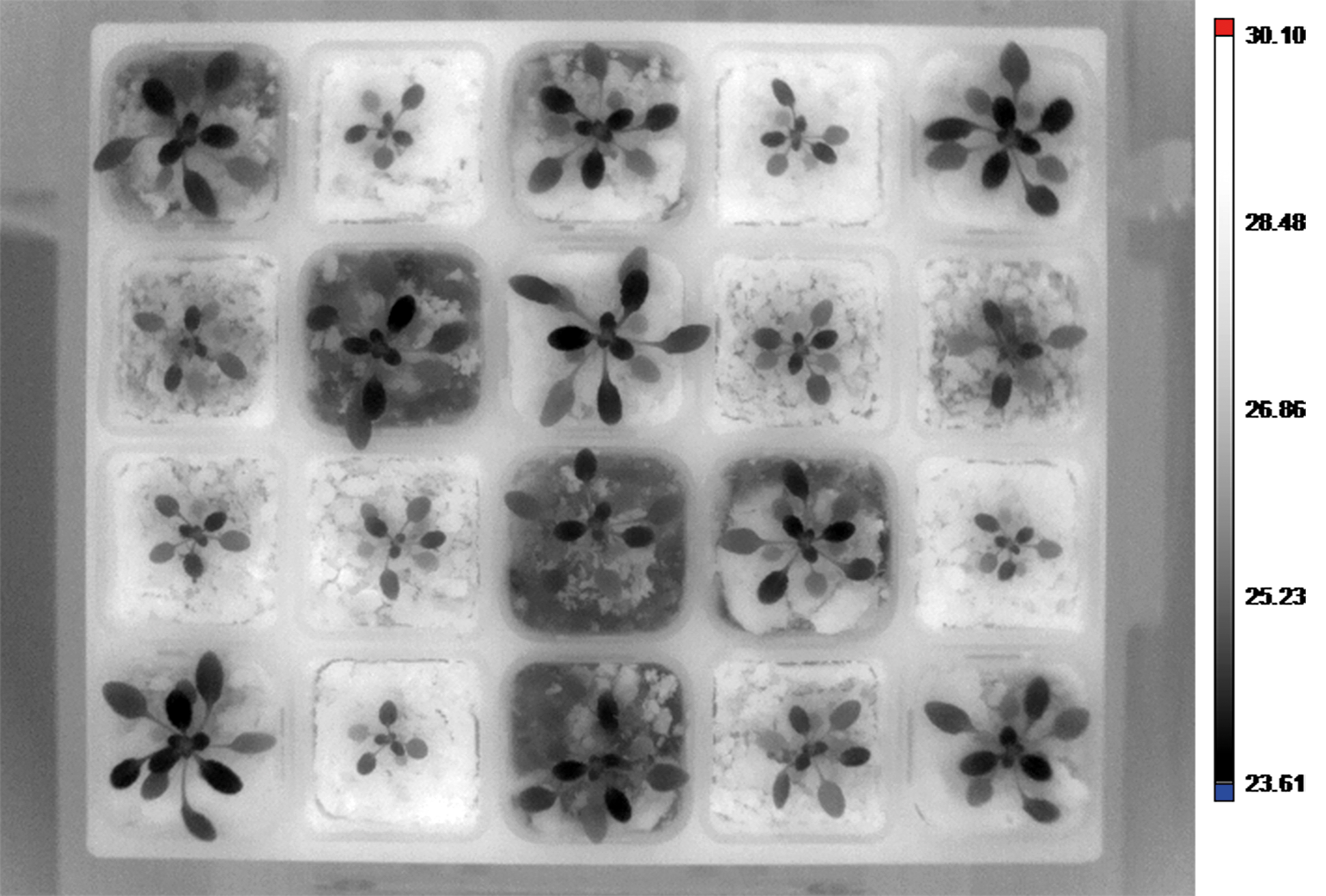
Thermal Imaging
Thermal cameras captures information in long-wavelenth infrared part of spectrum. Infrared radiation refers to the temperature of the imaged object and therefore can be used for non-invasively measurement of actual leaf and plant temperature. The temperature of the plant can be used as indicator of plant water-use efficiency, which relates to stomatal conductance and transpiration. Leaf temperature assesment is important for assessing a plant’s responses to heat load and water deprivation. Regulation of stomatal aperture to balance the opposing requirements of drought avoidance and self-cooling is critical to the survival of crops under extreme conditions. Variations in mechanisms for self-cooling may allow certain plants to better withstand periods of high irradiance and low water availability. High performance industrial infrared cameras are used that can be implemented both in top and side view configuration.
Key features
- Non-destructive measurement of plant and leaf temperature
- Dynamic measurement of infrared radiation emitted by all objects
- Highly homogenous LED light panel for active thermal image acquistion
- Top and side view configuration possible
- Rotating table for multiple angle thermal image acquisition
- Programmable measuring protocols.
- Automatic data analysis
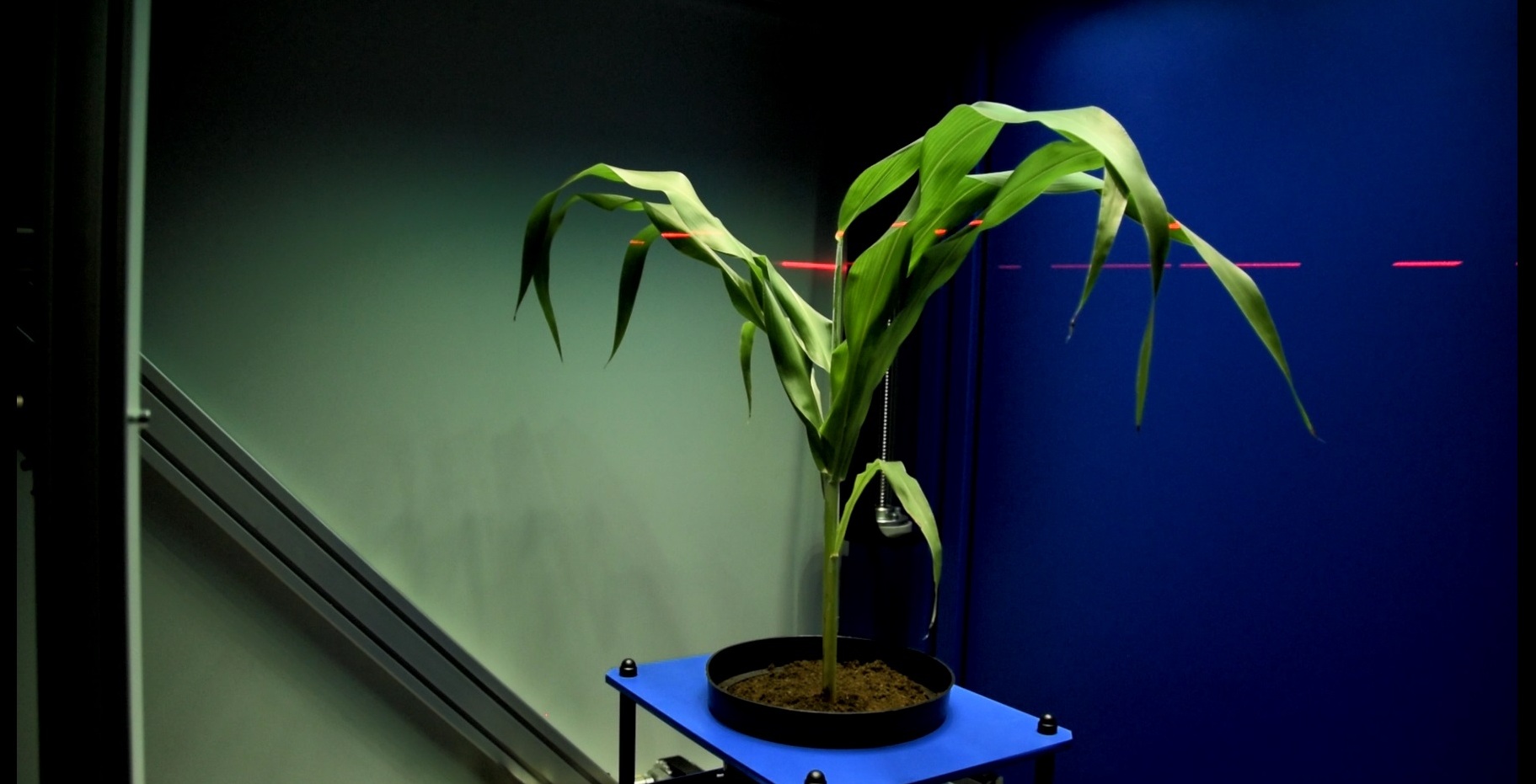
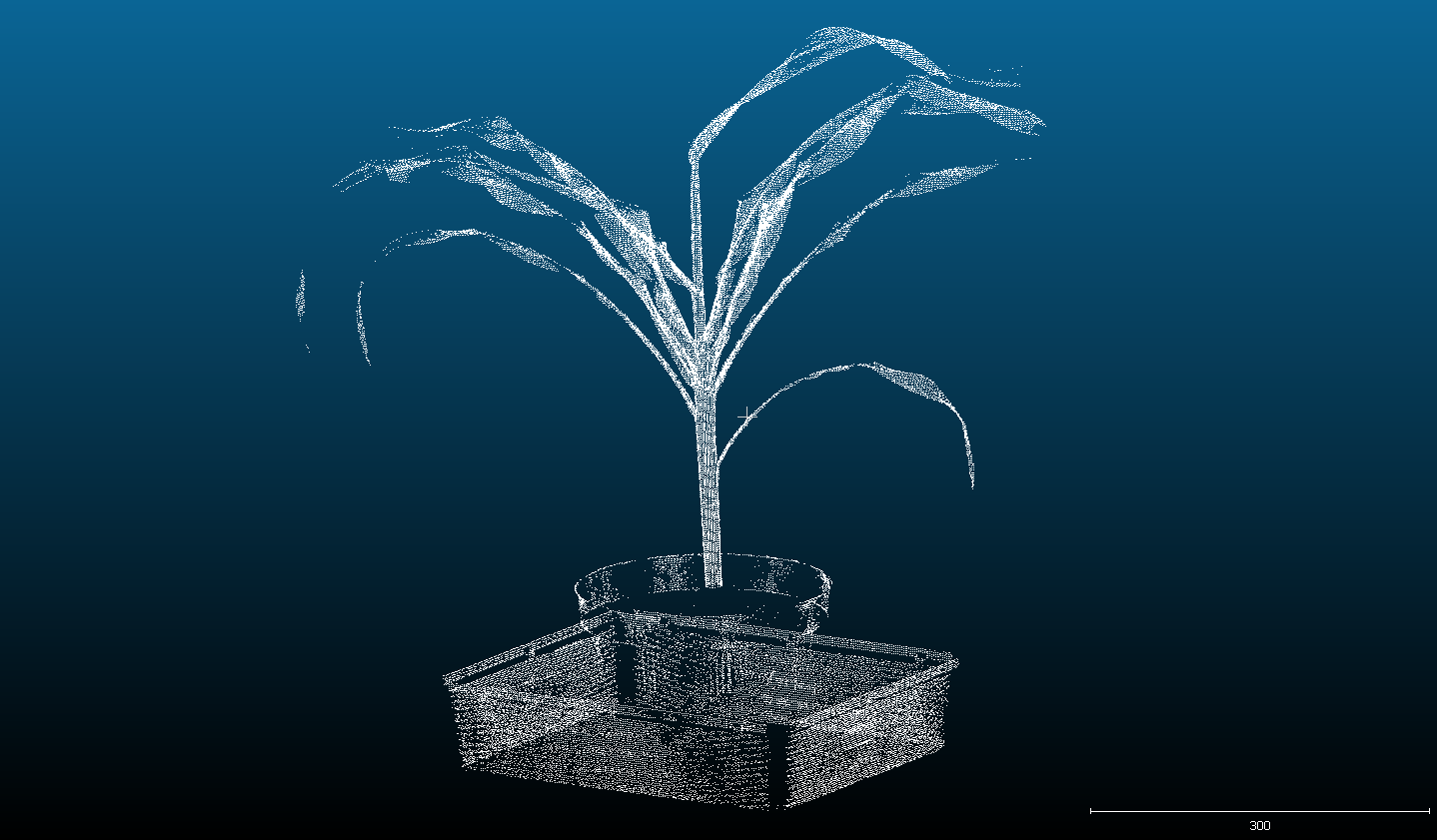
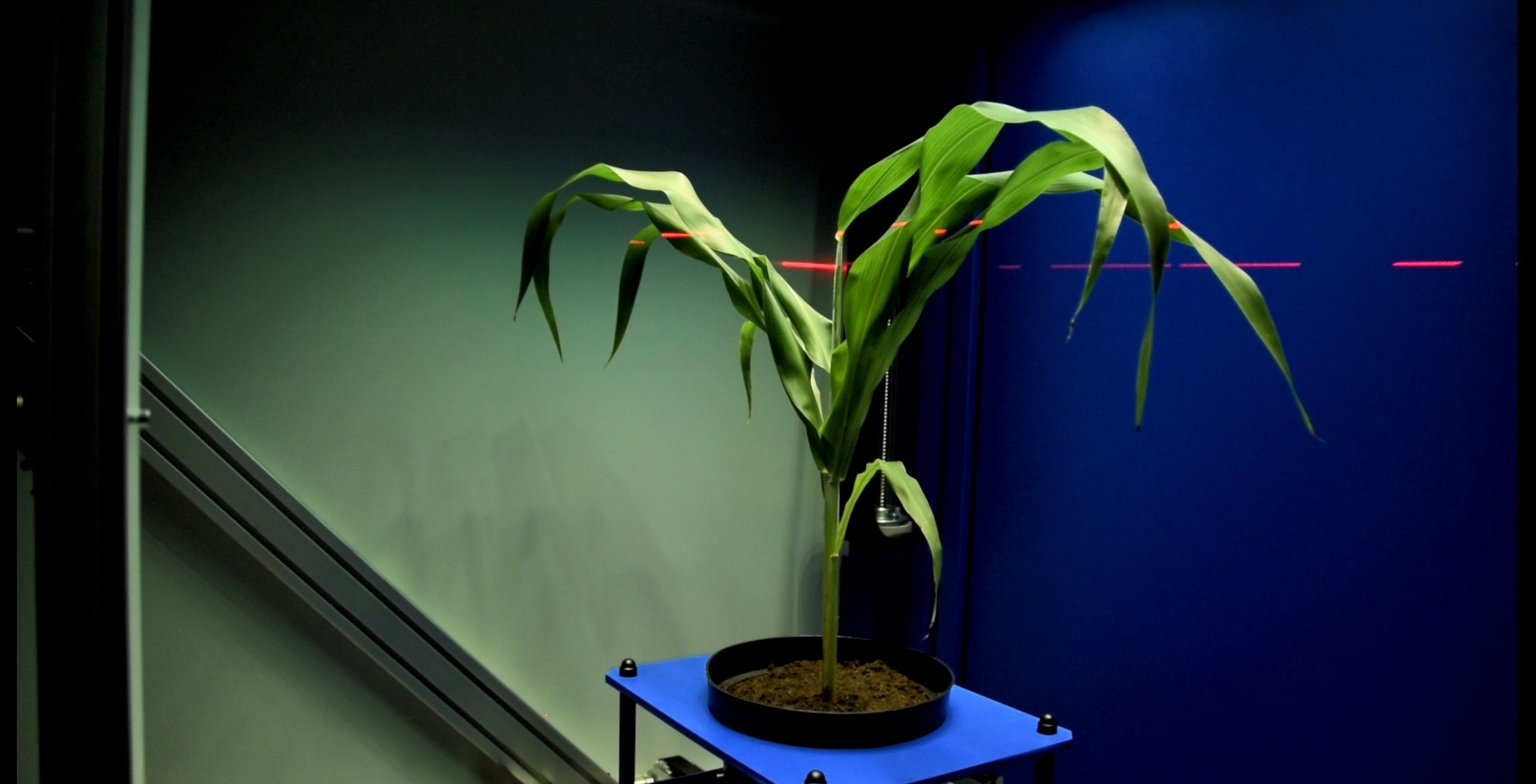
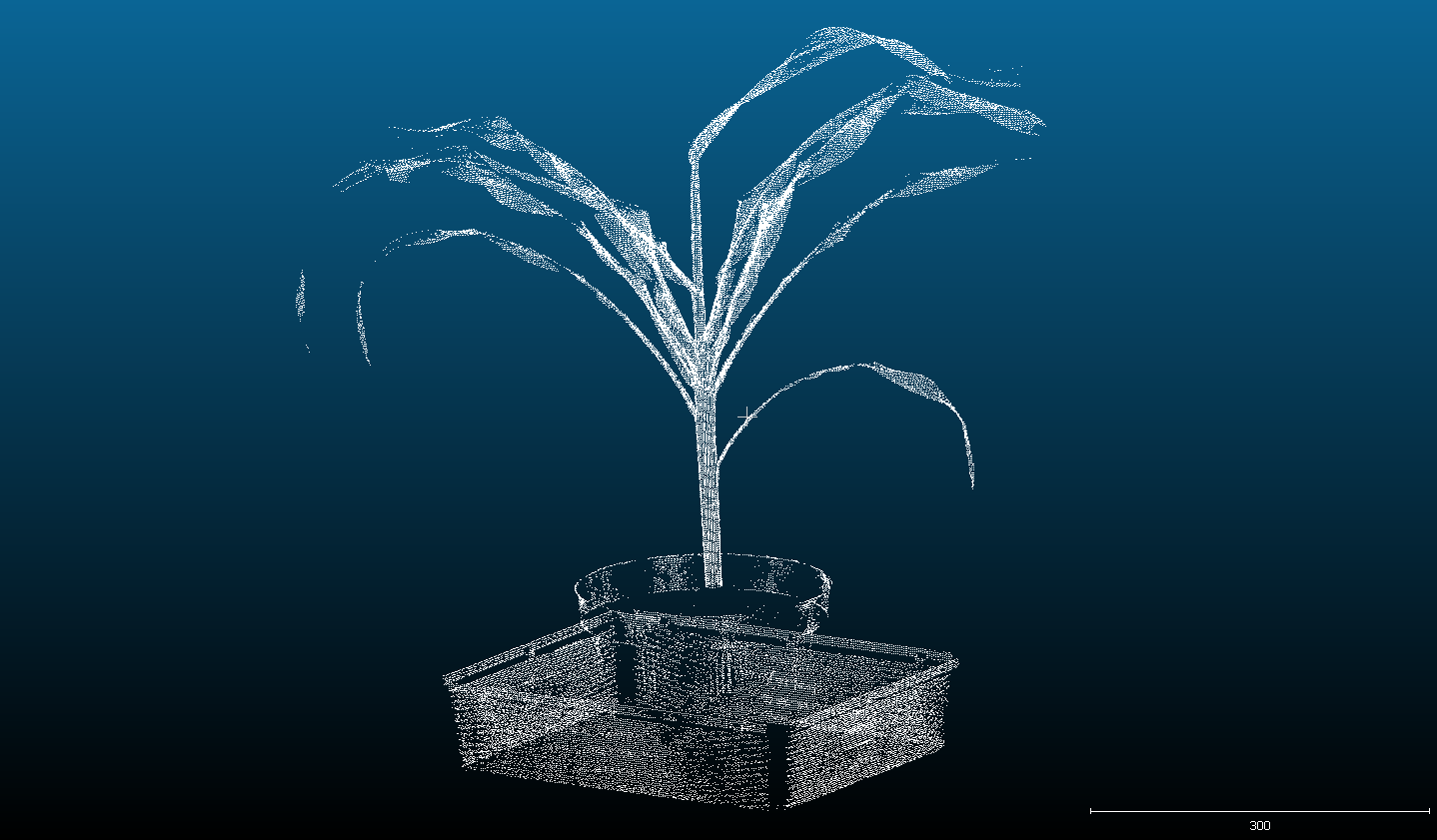
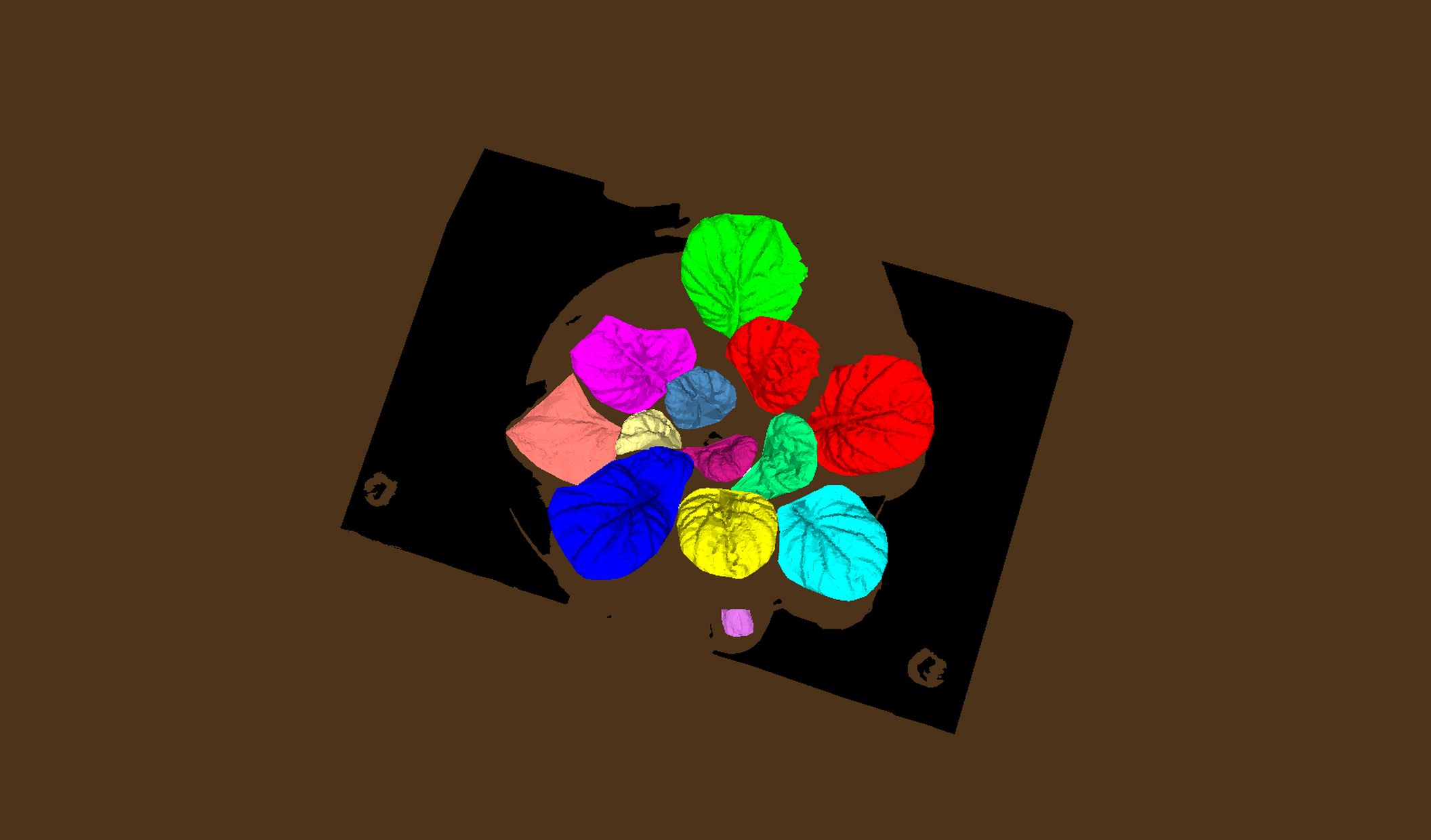
3D Scanning and modelling
3D laser scanner used in the PlantScreenTM Systems is designed for precise structural plant phenotyping. With the use of top and side scanning the precise plant 3D model is merged together. Based on the meshed models the automatic data analysis offers computations of a range ofmorphological parameters. For the best understanding of plant physiology the data from chlorophyl fluorescence measurement or from the colored CCD cameras are fitted to the 3D model. Systems are specifically and individually set up according the customers needs.
Key features
- Resolution less than 1mm
- Quick and effective approach of 3D modelling
- Top scan - scanning distance up to 60 cm
- Side scan - scanning distance is user defined
- Raw data in 3D point clouds
- Meshed models automatically analysed
- Projecting of chlorophyl fluorescence to 3D model
- Projecting of other model images to 3D
- Automatic analysis